Let’s discuss the question: shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors. We summarize all relevant answers in section Q&A of website Myyachtguardian.com in category: Blog MMO. See more related questions in the comments below.
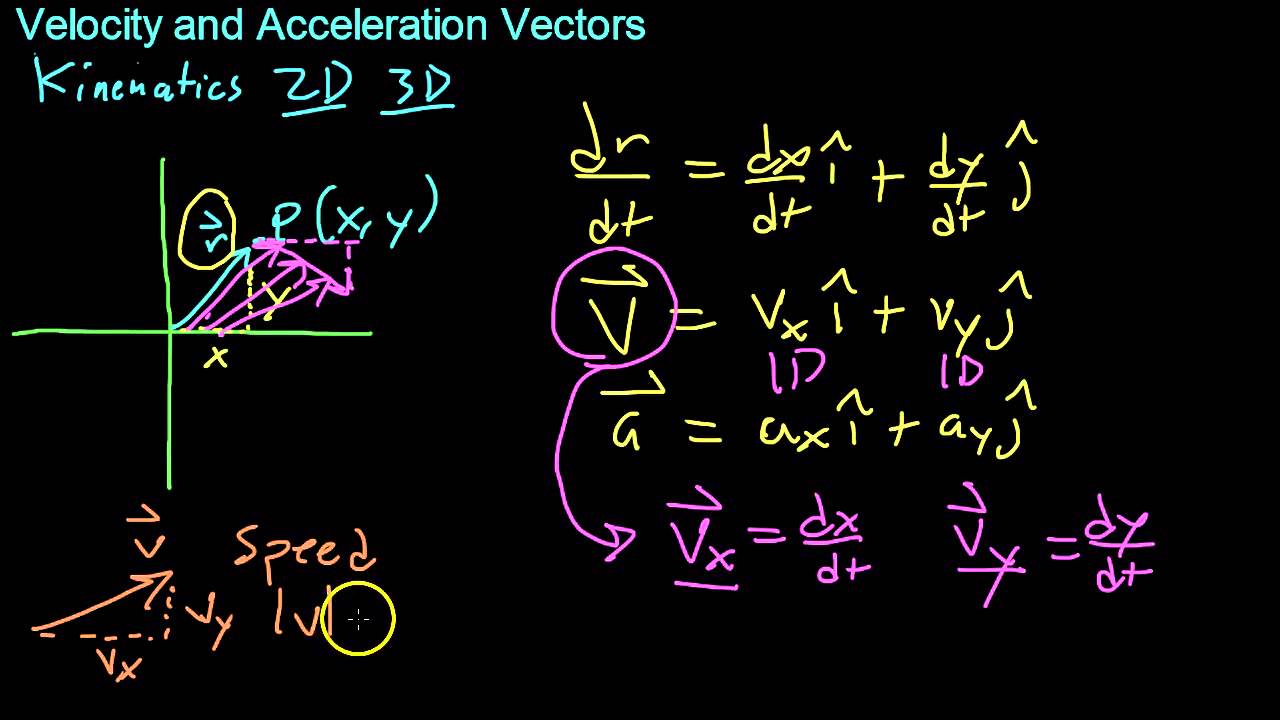
Table of Contents
What are velocity and acceleration vectors?
Velocity is a vector quantity which has a direction. The direction of the velocity vector is always in the direction which the object is moving. Direction of Acceleration: Acceleration is a vector quantity and it has a direction.
What is the vector for acceleration?
Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity.
Velocity and Acceleration Vectors
Images related to the topicVelocity and Acceleration Vectors

Can you add velocity and acceleration vectors?
Answer: No, because the two or more physical quantities can be added or subtracted only when they have same units, same nature eg. The addition is possible between distance and distance and you cannot add velocity and displacement.
How do you find the velocity vector?
Let r(t) be a differentiable vector valued function representing the position vector of a particle at time t. Then the velocity vector is the derivative of the position vector. v(t)=r′(t)=x′(t)ˆi+y′(t)ˆj+z′(t)ˆk.
What are velocity vectors?
A velocity vector represents the rate of change of the position of an object. The magnitude of a velocity vector gives the speed of an object while the vector direction gives its direction. Velocity vectors can be added or subtracted according to the principles of vector addition. velocity vectors magnitude.
How do you add velocity and acceleration?
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2). Acceleration is also a vector quantity, so it includes both magnitude and direction. Created by Sal Khan.
Find the Velocity and Acceleration Vectors Example Calculus 3
Images related to the topicFind the Velocity and Acceleration Vectors Example Calculus 3

When acceleration and velocity vectors are pointing in opposite directions?
If the velocity and acceleration are in the same direction (both have the same sign – both positive or both negative) the object is speeding up. If the velocity and acceleration are in opposite directions (they have opposite signs), the object is slowing down.
Why is velocity a vector?
Velocity has both magnitude and direction that is why it is a vector quantity. Whereas, Speed has only magnitude and no direction that is why it is a scalar quantity.
Is acceleration the derivative of velocity?
The derivative of position is velocity, the derivative of velocity is acceleration.
How do you find acceleration in calculus?
To find acceleration, we take the derivative of the velocity function. To determine the direction of the particle at t = 1 t=1 t=1, we plug 1 into the velocity function. Because v ( 1 ) v(1) v(1) is positive, we can conclude that the particle is moving in the positive direction (toward the right).
Is acceleration a vector or scalar?
For example, displacement, velocity, and acceleration are vector quantities, while speed (the magnitude of velocity), time, and mass are scalars. To qualify as a vector, a quantity having magnitude and direction must also obey certain rules of combination.
How the acceleration vector affects the velocity vector: qualitative change in speed and direction.
Images related to the topicHow the acceleration vector affects the velocity vector: qualitative change in speed and direction.

What is acceleration unit?
Unit of acceleration is the metre per second per second (m/s2). Definition. The snewton is that force which, when acting on a mass of one kilogramme, produces an acceleration of one metre per second per second.
What are the three types of velocity?
- Constant Velocity. An object with a constant velocity does not change in speed or direction. …
- Changing Velocity. Objects with changing velocity exhibit a change in speed or direction over a period of time. …
- Mathematics of Acceleration. …
- Instant Velocity. …
- Terminal Velocity.
Related searches
- an object has a position given by r = (2.0 m)
- while an object is in projectile motion with upward being positive with no air resistance
- george and harry dive from an overhang
- for general projectile motion when the projectile is at the highest point of its trajectory
- while an object is in projectile motion (with upward being positive) with no air resistance
- how to find velocity and acceleration vectors
- why are velocity and acceleration vectors
- shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors for an object in several
- if an object travels at a constant speed in a circular path, the acceleration of the object is
- for general projectile motion, when the projectile is at the highest point of its trajectory,
- if an object travels at a constant speed in a circular path the acceleration of the object is
- an object has a position given by r 2 0 m
- a rock is thrown at a window that is located 18 0 m above the ground
- a rock is thrown at a window that is located 18.0 m above the ground
- shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors for a person
Information related to the topic shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors
Here are the search results of the thread shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic shown below are the velocity and acceleration vectors. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.

