Let’s discuss the question: how should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization. We summarize all relevant answers in section Q&A of website Myyachtguardian.com in category: Blog MMO. See more related questions in the comments below.
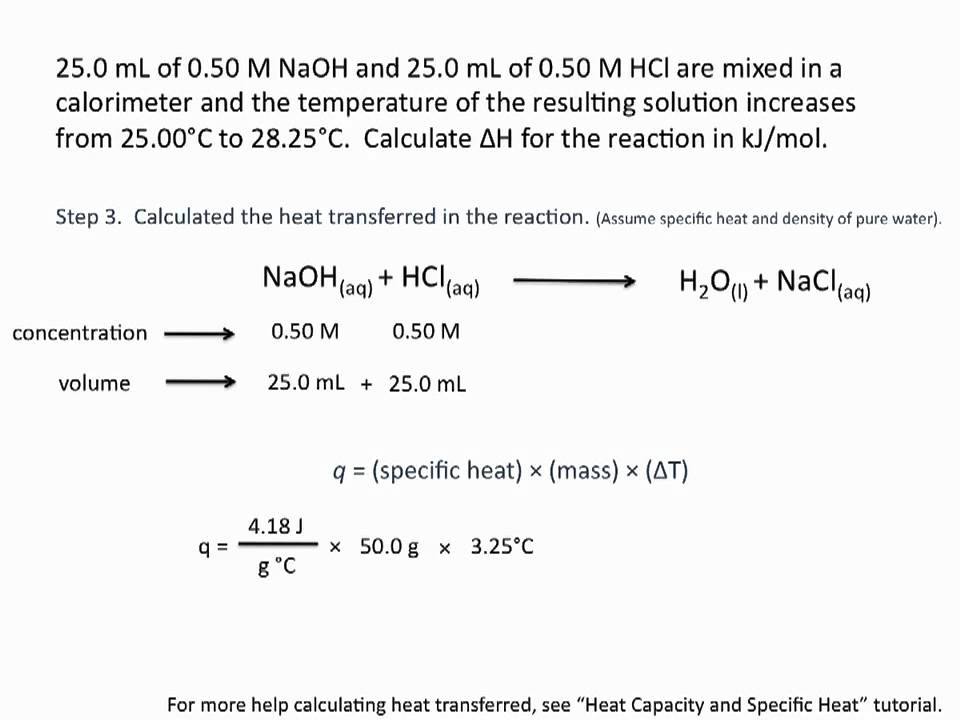
Table of Contents
How should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization of NaOH and the two acids compare why quizlet?
how should the two heats of reactions for the neutralization of NaOH and the two acids compare? the heat of the stronger acid should be greater than the weaker acid because strong acids dissociate 100% in an aqueous solution.
What is the heat of reaction for a neutralization reaction?
The heat (or enthalpy) of neutralization (ΔH) is the heat evolved when an acid and a base react to form a salt plus water. Q in the above equation is -ΔH and is expressed in kJ/mol of water.
Using Calorimetry to Calculate Enthalpies of Reaction – Chemistry Tutorial
Images related to the topicUsing Calorimetry to Calculate Enthalpies of Reaction – Chemistry Tutorial

Why is the heat of neutralization the same?
Enthalpy of neutralization is always constant for a strong acid and a strong base: this is because all strong acids and strong bases are completely ionized in dilute solution. Enthalpy changes in neutralization are always negative-when an acid and alkali react, heat is given out.
Does a neutralization reaction require heat?
For weak acids or bases, the heat of neutralization is pH-dependent. In the absence of any added mineral acid or alkali some heat is required for complete dissociation. The total heat evolved during neutralization will be smaller. The heat of ionization for this reaction is equal to (–12 + 57.3) = 45.3 kJ/mol at 25 °C.
What factors impact heat evolved by a neutralization reaction?
…
Heat change of neutralization reaction is affected by 3 factors:
- Quantity of acid and alkali.
- Basicity of the acid and alkali.
- Strength of acid and alkali.
What is the value of specific heat of water?
The exact value of the specific heat capacity of water is 4182 J/kg°C.
Is heat absorbed during neutralization?
Answer: The heat (or enthalpy) of neutralization (ΔH) is the heat evolved when an acid and a base react to form a salt plus water. Q in the above equation is -ΔH and is expressed in kJ/mol of water. … The heat (Q) given off by the neutralization reaction is absorbed by the reaction solution and the calorimeter.
How much heat is released by the neutralization reaction in kJ?
Enthalpy changes of neutralization are always negative – heat is released when an acid and and alkali react. For reactions involving strong acids and alkalis, the values are always very closely similar, with values between -57 and -58 kJ mol–1.
How do you calculate heat of neutralization?
Calculate the heat of neutralization using the fomula Q = mcΔT, where “Q” is the heat of neutralization, “m” is the mass of your acid, “c” is the specific heat capacity for aqueous solutions, 4.1814 Joules(grams x °C), and “ΔT” is the change in temperature you measured using your calorimeter.
Neutralization Reactions
Images related to the topicNeutralization Reactions
How does concentration affect neutralization?
Explanation: In an acid or basic solution, the concentration expresses how much acid or base is dissolved there. To neutralize acids, you need equal amounts of base, and vice-versa, and therefore more concetrated solutions require more of the reagent.
When both acid and base are strong the heat of neutralization is?
The enthalpy of neutralization of any strong acid and strong base is always constant, i.e. 57.1 kJ because both the acid and base undergo complete ionization.
What type of reaction is a neutralization reaction?
A neutralization is a type of double replacement reaction. A salt is the product of an acid-base reaction and is a much broader term then common table salt as shown in the first reaction.
Is heat of neutralization exothermic or endothermic?
Enthalpy of neutralization is always exothermic.
What factors affect neutralization?
The factors that affect neutralisation: – The concentration of the acid – The strength of the acid – The strength of the alkali – The temperature Preliminary Investigation We carried out a preliminary experiment to find the best conditions to carry out an investigation to determine how concentration affects the volume …
Are neutralization reactions exothermic?
1 Answer. Acid base neutralization involves the formation of a salt and water. Such a process is inevitably exothermic.
What is specific latent heat?
The specific latent heat of fusion LF of a substance is the energy needed to change the state of 1kg of the substance from a solid to a liquid, at its melting point (without changing the temperature).
Why specific heat capacity of water is high?
Water’s high heat capacity is a property caused by hydrogen bonding among water molecules. When heat is absorbed, hydrogen bonds are broken and water molecules can move freely. When the temperature of water decreases, the hydrogen bonds are formed and release a considerable amount of energy.
Lab Experiment #17: Heat of Neutralization.
Images related to the topicLab Experiment #17: Heat of Neutralization.

Why is the specific heat of water higher than ice?
As a liquid, water has more directions to move and to absorb the heat applied to it. There is more surface area that needs to be heated for the overall temperature to increase. However, with ice, the surface area doesn’t change due to its more rigid structure.
Is heat absorbed or evolved in neutralization reaction?
The heat (or enthalpy) of neutralization (ΔH) is the heat evolved when an acid and a base react to form a salt plus water. Q in the above equation is -ΔH and is expressed in kJ/mol of water. Neutralization reactions are generally exothermic and thus ΔH is negative.
Related searches
- heat of neutralization
- heat of neutralization lab report
- how should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization of naoh and the two acids compare
- what is the largest source of error in the experiment heat of neutralization
- a 50.0 ml sample of a 1.00 m solution of cuso4 is mixed with 50.0 ml of 2.00 m koh in a calorimeter
- heat of neutralization of hcl and naoh experiment
- a 50 0 ml sample of a 1 00 m solution of cuso4 is mixed with 50 0 ml of 2 00 m koh in a calorimeter
- how to calculate heat of neutralization
- the experimental procedure has you wash your thermometer and dry
- heat of neutralization theory
Information related to the topic how should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization
Here are the search results of the thread how should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic how should the two heats of reaction for the neutralization. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.

